When your vehicle is in an accident, choosing a shop that follows OEM-approved repair procedures is critical.
Some shops cut corners. Others follow the factory rulebook. Some shops follow procedures based on habit, outdated techniques, or cost-saving shortcuts. Others adhere strictly to OEM-approved repair procedures — the same ones the vehicle’s manufacturer outlines to ensure safety, performance, and proper function.
If your shop is not following OEM repair procedures, your vehicle may look fine on the outside but fail when it matters most.
What Are OEM-Approved Repair Techniques?
Top Questions People Ask:
- What’s the difference between OEM and aftermarket parts?
- Why are OEM parts and procedures important in collision repair?
- How do I know if a body shop uses OEM-approved repair techniques?
OEM-approved repair procedures are repair steps and protocols published by the original vehicle manufacturer. These procedures are based on engineering and crash testing to ensure that every repair restores the vehicle to its pre-accident safety and performance standards.
Examples include:
- Welding specifications — such as squeeze-type resistance spot welds (STRSW) or MIG plug welds at designated locations
- Structural sectioning rules — with clear guidelines on where to cut and where not to
- Adhesives, seam sealers, and corrosion protection — based on materials used in the original build
- Replacement vs. repair criteria — for high-strength steel, aluminum, or composite components
These procedures are not suggestions. According to I-CAR and multiple OEM position statements, deviation from published procedures compromises vehicle integrity and can result in serious safety risks.
“Failure to follow OEM procedures will sacrifice the safety and quality of the repair.”
— Repairer Driven News, citing Toyota/Lexus structural repair guidelines
Why Following OEM Procedures Matters
1. Safety
To begin with, modern vehicles are designed as integrated safety systems. Crumple zones, airbag sensors, seatbelt tensioners, and advanced materials all work together during a crash. If a technician uses the wrong welding method or sectioning location, the car may not protect occupants as designed in a future accident.
2. Resale Value
In addition, cars repaired to OEM specs hold their value better. Poor panel alignment, mismatched paint, or signs of shortcut work raise red flags for buyers and appraisers. A well-repaired vehicle is often indistinguishable from factory-new, especially when OEM parts are used and procedures are followed.
3. Warranty Compliance
Furthermore, many OEMs state that the use of aftermarket or recycled parts can void corrosion and structural warranties. Even if a repair does not cause failure immediately, improper procedures might void coverage for future issues.
4. Legal and Insurance Protections
In California, OEM procedures are considered the industry standard. The California Bureau of Automotive Repair (BAR) requires that repairs be completed per OEM service specs or nationally accepted standards.
Translation: cutting corners is not only risky — it may be illegal.
Risks of Non-OEM Repairs
Shops that do not follow OEM guidelines might:
- Use non-approved welds or bonding methods, weakening structural areas
- Section frames or pillars in locations where cuts are prohibited
- Skip corrosion protection steps, leading to rust damage months later
- Install aftermarket or salvage parts that are not crash-tested for your vehicle
- Ignore recalibrations for airbags or ADAS systems
These shortcuts increase the risk of safety system failures, diminished value, and re-repairs. Studies show that most comeback repairs could be avoided by following OEM instructions.
Certified vs. Non-Certified Collision Repair Shops
Related Questions:
- Is it better to choose a certified collision repair center?
- What certifications should a good body shop have?
OEM-certified shops must:
- Use brand-approved tools and equipment
- Employ technicians trained specifically for each brand
- Access current OEM repair databases (e.g., Tesla Toolbox, BMW ISTA, LexusTech)
- Only use new OEM parts
As a result, non-certified shops may lack this training or use generic repair methods. Certification also helps maintain warranty protection and increases repair accountability.
What California Law Says
Common Search:
- Do insurance companies pay for OEM parts?
- Can I request OEM parts for my car repair?
- Will using aftermarket parts void my warranty?
Under California regulations:
- Repair shops must disclose part type and origin (OEM, aftermarket, used)
- Insurers must cover all repairs required to restore pre-loss condition — including OEM-required steps
- Using aftermarket parts without written consent is illegal
- OEM specifications set the industry standard for proper collision repairs.
If a shop or insurer pushes back against OEM procedures, they may be violating state law.

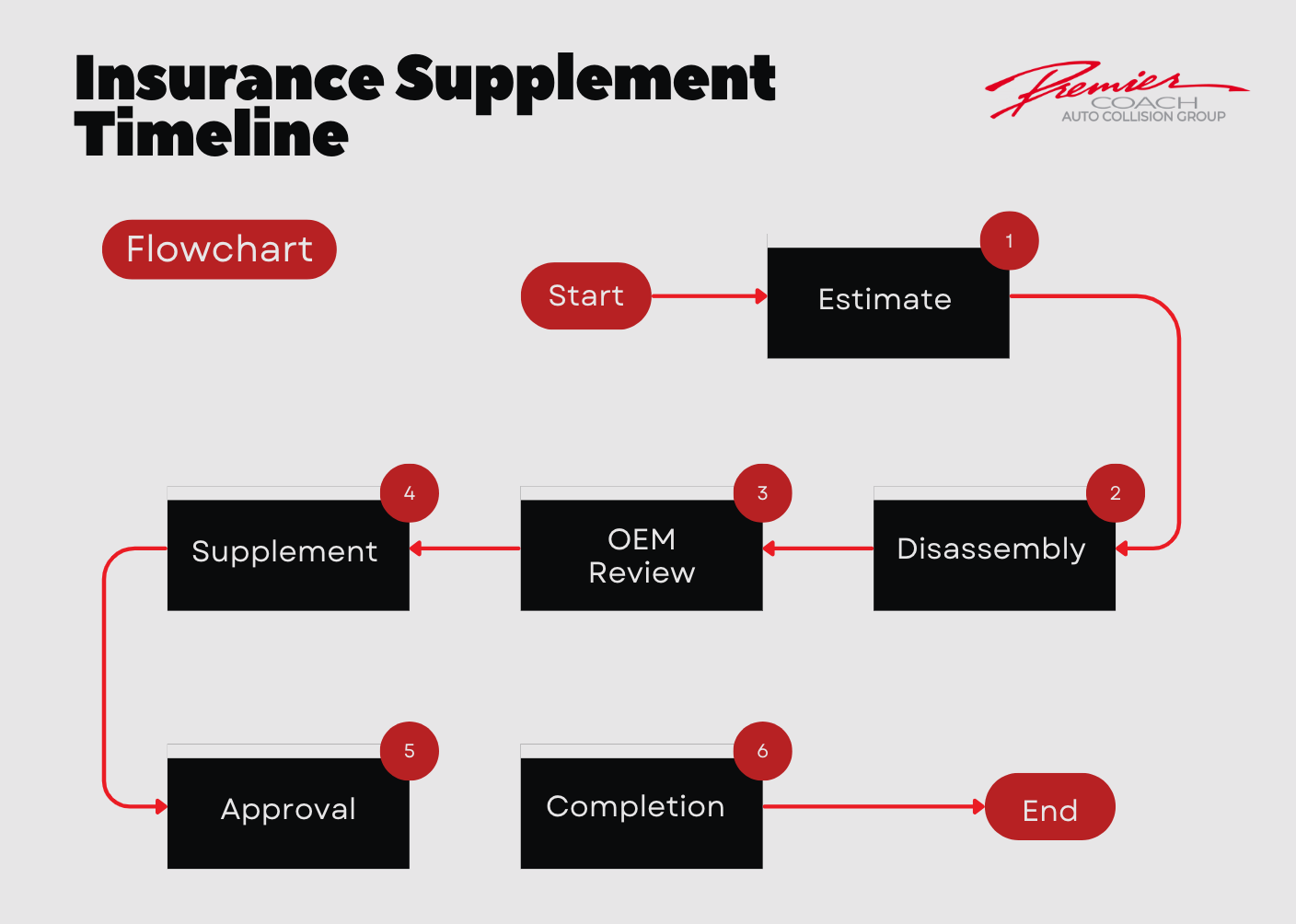
The Insurance Supplement Process
Often, insurance estimates miss important OEM-required steps until disassembly. Quality shops submit supplements— documented requests for additional labor, parts, or procedures that align with OEM instructions.
A strong repair partner:
- Reviews OEM procedures for your vehicle make/model
- Documents hidden damage or missed operations
- Communicates directly with insurers to explain the supplement
Ultimately, this approach ensures a complete and safe repair — not just the cheapest fix.
Industry Trends and Data
- The average repairable claim exceeded $3,700 in 2022, up over 39% from 2019 — due in part to OEM-required scans and materials.
- Nearly 60% of repairable vehicles now require diagnostic scans or calibrations.
- Worst of all, improper sectioning or bonding can lead to catastrophic failures in future crashes.
How Premier Coach Auto Collision Does It Right
At Premier Coach Auto Collision, we follow one rule: repair every vehicle to manufacturer specifications — every time.
That is why our facilities in Thousand Oaks and Camarillo are certified by brands like Tesla, BMW, Lexus, and many others.
To consistently meet those standards, we invest in:
-
Ongoing OEM-specific training to keep our technicians up to date
-
Direct access to factory repair platforms and documentation for accurate procedures
-
OEM-only parts — never aftermarket or recycled substitutes
-
Thorough insurance supplement support, including documentation and approvals
When guests come to Premier Coach, they leave with the confidence that their vehicle has been repaired the right way — backed by a lifetime warranty.
Ask the Right Questions
Final Takeaway Questions:
- How do OEM repair methods affect my car’s safety and value?
- Does using non-OEM parts affect resale value?
To summarize, not every collision repair shop uses OEM-approved repair techniques — but you have the right to demand them.
 At Premier Coach Auto Collision, this commitment is non-negotiable. We ensure every repair follows manufacturer guidelines to preserve your vehicle’s safety, value, and warranty. Whether you drive a Tesla, Lexus, BMW, or any other certified brand, our team uses only OEM parts and factory-approved procedures — no shortcuts, ever.
At Premier Coach Auto Collision, this commitment is non-negotiable. We ensure every repair follows manufacturer guidelines to preserve your vehicle’s safety, value, and warranty. Whether you drive a Tesla, Lexus, BMW, or any other certified brand, our team uses only OEM parts and factory-approved procedures — no shortcuts, ever.
Ask your body shop these critical questions before you approve any repairs:
-
First, confirm they follow OEM repair procedures for your specific vehicle.
-
Next, ask if their technicians hold certifications from your vehicle’s manufacturer.
-
Then, make sure they use only new OEM parts — not aftermarket or recycled substitutes.
-
Finally, find out how they manage insurance supplements and secure full repair coverage.
Your safety, warranty, and vehicle value all depend on getting the right answers.
If you want certified, OEM-approved collision repair in Ventura County, trust Premier Coach Auto Collision to get it done right.

